Introduction
World Pneumonia Day, observed every year on November 12, is an opportunity to focus global attention on pneumonia, a preventable and treatable illness that remains one of the leading causes of death for young children and the elderly worldwide. This day aims to educate, advocate, and mobilize support to reduce pneumonia-related deaths through increased awareness, vaccination, and healthcare access.
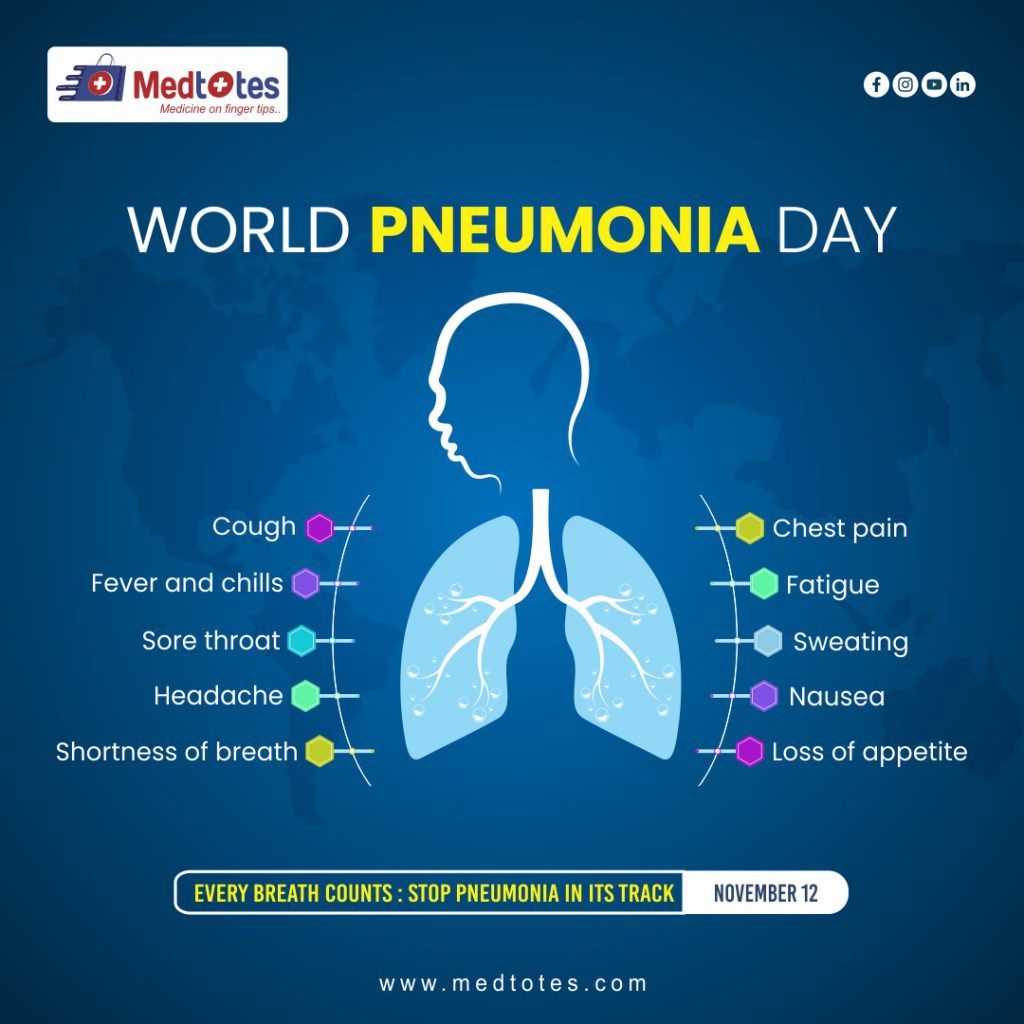
Causes and Symptoms of Pneumonia
Pneumonia is a lung infection that can be caused by various pathogens, including bacteria, viruses, and fungi. The most common bacterial cause is Streptococcus pneumoniae, while viruses like influenza and respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) are also significant contributors. In some cases, fungi, especially in people with weakened immune systems, can lead to pneumonia.
Symptoms of pneumonia can vary depending on the cause and severity but often include:
- Cough (which may produce phlegm)
- Fever and chills
- Shortness of breath
- Chest pain when breathing or coughing
- Fatigue and weakness
In young children, elderly adults, and people with chronic health conditions, symptoms may be more severe and can quickly worsen if left untreated. This is why early detection and access to medical care are crucial, particularly in vulnerable populations.
Prevention and Treatment of Pneumonia
Pneumonia is both preventable and treatable, and prevention is one of the best ways to protect vulnerable populations. Key preventive measures include:
- Vaccination: Vaccines are among the most effective tools to prevent pneumonia. The pneumococcal vaccine protects against bacterial pneumonia caused by Streptococcus pneumoniae, while the influenza vaccine can help reduce the risk of viral pneumonia.
- Hygiene and Clean Air: Washing hands regularly, using masks when appropriate, and avoiding smoking can reduce exposure to pathogens that cause pneumonia. Clean air is essential; reducing indoor air pollution, often caused by wood-burning stoves or secondhand smoke, can lower the risk of respiratory infections.
- Nutrition and General Health: Good nutrition supports a strong immune system that can effectively fight infections. Access to healthy food and supplements, especially in developing areas, is crucial for at-risk groups.
- Access to Medical Care: Early treatment can prevent pneumonia from becoming severe or life-threatening. Antibiotics, antivirals, or antifungals may be prescribed depending on the cause, and supportive care, like oxygen therapy, may be needed for severe cases.
Treatment varies depending on the type of pneumonia. For bacterial pneumonia, antibiotics are usually prescribed. Viral pneumonia may require antiviral medications, while antifungal medications are used for fungal infections. The sooner treatment begins, the better the chances of recovery, particularly for high-risk individuals.
Conclusion
On World Pneumonia Day, we’re reminded that pneumonia is a preventable and treatable illness, yet it remains a global health issue claiming the lives of vulnerable individuals every year. Through education, advocacy, and support for preventive measures like vaccination and access to clean air, we can make significant strides in reducing the global impact of this disease.
